Monday, September 05, 2005
BIOLOGY - Leaf Structure
~LEAF STRUCTURE~
- main organ where photosynthesis occurs
- adapted for photosynthesis
.:INTERNAL FEATURES:.
CUTICLE
transperant wax covering
-protect leaf
-prevent excessive loss of water
-focuses light to mesophyll
EPIDERMIS
Upper- single layer of cells
-secretes cuticle
Lower- layer of cells that protects lower part of leaf
stomata - surrounded by guard cells
MESOPHYLL- main site of photosynthesis
contains numerous chloroplasts
Palisade Mesophyll
closely packed
elongated
tapered end
first cells to recieve light during photosynthesis
20-30 chloroplasts
Spongy Mesophyll
spherical
loosely arranged
surrounding large intercellular spaces
layer of moisture around cells
some photosynthesis
allow gases to freely diffuse throughout leaf
Xylem - dead cells
bring water and dissolved minerals TO the leaf
strengthen leaf
resist tearing
Phleom
transport sucrose AWAY from the leaf
transport amino acids TO AND FROM the leaf
Intercellular spaces
gaseous exchange
CO2
Guard cells
1-3 chloroplast
uneven cell wall (thin wall will curve more)
response to internal pressure of guard cells
- affected by light intensity and rate of evaporation
control CO2 entry/water loss
-----------------------
photosynthesis -> glucose formed (concentration gradient)
water potential in cells will DROP
water move into guard cells (osmosis)
guard cells INCREASE in volume
expands (become turgid)
stoma open (uneven curvature)
----------------------
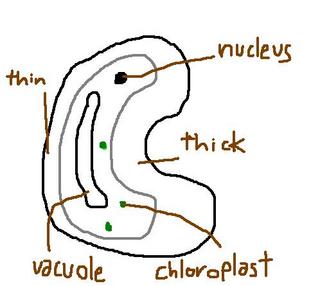
--guard cell
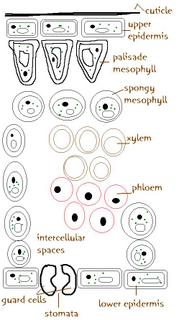
-- leaf cross section
=======================================================
.:EXTERNAL FEATURES:.
Petiole
-hold leaf towards sun
Board lamina
-incerase surface area for light absorption
Thin lamina
- facilitate gaseous exchange and light penetration
Venation
- transport of substances
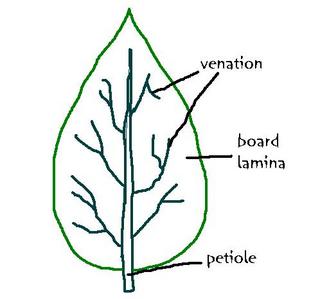
--external features of a leaf
- main organ where photosynthesis occurs
- adapted for photosynthesis
.:INTERNAL FEATURES:.
CUTICLE
transperant wax covering
-protect leaf
-prevent excessive loss of water
-focuses light to mesophyll
EPIDERMIS
Upper- single layer of cells
-secretes cuticle
Lower- layer of cells that protects lower part of leaf
stomata - surrounded by guard cells
MESOPHYLL- main site of photosynthesis
contains numerous chloroplasts
Palisade Mesophyll
closely packed
elongated
tapered end
first cells to recieve light during photosynthesis
20-30 chloroplasts
Spongy Mesophyll
spherical
loosely arranged
surrounding large intercellular spaces
layer of moisture around cells
some photosynthesis
allow gases to freely diffuse throughout leaf
Xylem - dead cells
bring water and dissolved minerals TO the leaf
strengthen leaf
resist tearing
Phleom
transport sucrose AWAY from the leaf
transport amino acids TO AND FROM the leaf
Intercellular spaces
gaseous exchange
CO2
Guard cells
1-3 chloroplast
uneven cell wall (thin wall will curve more)
response to internal pressure of guard cells
- affected by light intensity and rate of evaporation
control CO2 entry/water loss
-----------------------
photosynthesis -> glucose formed (concentration gradient)
water potential in cells will DROP
water move into guard cells (osmosis)
guard cells INCREASE in volume
expands (become turgid)
stoma open (uneven curvature)
----------------------

--guard cell

-- leaf cross section
=======================================================
.:EXTERNAL FEATURES:.
Petiole
-hold leaf towards sun
Board lamina
-incerase surface area for light absorption
Thin lamina
- facilitate gaseous exchange and light penetration
Venation
- transport of substances

--external features of a leaf